![Symptoms of ovarian laziness in ultrasound [treatment method] | Dr. Shiva Madani](/storage/https://drshivamadani.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/5-12.jpg)
Symptoms of ovarian laziness in ultrasound [treatment method] | Dr. Shiva Madani

Symptoms of ovarian laziness in ultrasound
07/23/1404
Ovarian laziness or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders among women of reproductive age that can affect the menstrual cycle, fertility, and even physical appearance. One of the most accurate ways to diagnose this problem is pelvic ultrasound. In this imaging examination, the doctor can observe the structure of the ovaries and evaluate the presence of symptoms such as multiple follicles, an increase in the volume of the ovary or a thickening of the wall. Affected women usually go to the doctor with symptoms such as irregular periods, hair growth, acne or difficulty in pregnancy, and ultrasound is a tool that helps confirm the diagnosis and check the severity of the disease. In fact, the clear ultrasound image not only shows the current state of the ovary, but also makes the treatment path clearer for the doctor. Familiarity with the symptoms of this complication in ultrasound can help early diagnosis and better control of symptoms.
Symptoms of ovarian laziness in ultrasound
Ultrasound is one of the most accurate and at the same time the simplest methods to check the health of the ovaries. In women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), the structure and tissue of the ovaries changes, and these changes can be clearly seen in ultrasound. In this examination, the doctor looks for symptoms such as ovarian enlargement, an increase in the number of small follicles, and thickening of the wall. These symptoms, along with clinical symptoms such as irregular periods or acne, can confirm the diagnosis of ovarian laziness.
Definition of ovarian indolence or PCOS
Ovarian laziness is actually a hormonal disorder in which the ovaries do not ovulate properly. This problem causes the eggs to get stuck in the follicles and the menstrual cycle is irregular or sometimes interrupted. At the hormonal level, the body experiences an increase in androgen (male hormone), which causes excess hair and acne. PCOS is a common but controllable disease whose early diagnosis plays an important role in preventing infertility.
The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of PCOS
Ultrasound is one of the most important diagnostic tools for ovarian laziness. Unlike a blood test that only shows hormone levels, an ultrasound provides a clear picture of the structure of the ovaries. In this image, the doctor can evaluate the number of follicles, the size of each ovary and the state of its capsule. If the number of small follicles is high and the ovary becomes swollen, the possibility of PCOS is very high. In many cases, this ultrasound image is the first warning for a more detailed examination.
The normal structure of the ovary in ultrasound
To better understand the changes caused by ovarian laziness, you must first understand the normal appearance of the ovary. A healthy ovary usually contains several follicles of different sizes, one of which grows and is released in each menstrual cycle. In ultrasound, a healthy ovary has a size between 3 and 5 cm and its wall is thin and uniform. The distribution of follicles in a normal ovary is irregular but balanced, and no abnormal accumulation is seen around the tissue.
Difference between healthy and lazy ovary in ultrasound
In ultrasound, the difference between a healthy ovary and a lazy one is quite evident. Ovaries with PCOS are usually larger than normal and numerous tiny follicles are seen on its periphery. These follicles are regularly arranged around the ovary and create a pearl necklace-like appearance. The wall of the ovary is also thicker and this change in tissue shows that the eggs are not able to leave the follicle. This pattern is considered to be the image signature of ovarian laziness in ultrasound.
Observation of multiple follicles in ultrasound
One of the most obvious symptoms of PCOS is the presence of more than 12 small follicles in each ovary. These follicles usually have a diameter of less than 10 mm and do not reach full maturity. At first glance, they may be seen as round and dark spots on the periphery of the ovary. In healthy women, such follicles disappear at the end of each cycle, but in affected people, these follicles remain and over time cause an increase in the size of the ovary.
Ovarian volume increase in ultrasound
An increase in ovarian size is another sign of ovarian laziness. Doctors usually consider a volume of more than 10 ml to be abnormal. The reason for this increase in volume is the accumulation of follicles and thickening of the surrounding tissue. However, ovarian enlargement alone is not a definitive sign and should be evaluated along with other findings. The important point is that in some women, only one of the ovaries is larger than usual, and this case can make the diagnosis more accurate.
What is the thick wall of the ovary
?In ultrasound, the thickening of the ovarian capsule is a sign of ovulation disorder. The thick wall is actually a physical barrier that does not allow the egg to leave the follicle. This causes the eggs to get stuck inside the follicle and disrupts the normal cycle of ovulation. This feature is usually seen alongside multiple follicles and helps the doctor make a more accurate diagnosis. The thickening of the ovarian capsule is one of the specific symptoms of PCOS.
Image of polycystic ovary in ultrasound
In ultrasound, polycystic ovary has a special and well-known appearance. Tiny follicles are seen in the periphery of the ovary in a regular, ring-like pattern, while the center of the ovary is usually relatively empty and lighter. Doctors liken this pattern to a "pearl necklace". Such an image is usually accompanied by an increase in the volume and thickness of the wall, making the diagnosis much more certain. This visual pattern is so clear that in many cases, the possibility of PCOS is raised even before laboratory examination.

The right time to do ovarian ultrasound
The time of ultrasound plays a big role in the accuracy of diagnosis. The best time is usually the third to fifth day of the menstrual cycle, because at this time the follicles are smaller and more clearly visible. If the ultrasound is performed late in the cycle, the dominant follicle may hide other follicles and make the diagnosis difficult. Therefore, doctors usually prescribe ultrasound at the beginning of the menstrual cycle to check the true state of the ovaries. In women with irregular periods, the time of ultrasound is determined according to the hormonal status.
In this section, we learned about the main signs of ovarian laziness in ultrasound and how to interpret it. In the next section, we go to deeper topics; From the correlation of ultrasound results with hormones and blood tests to differential diagnosis and the role of lifestyle in improving symptoms.
Physical symptoms related to the ultrasound image
The ultrasound image is only part of the story. Clinical signs such as excessive hair growth, acne, abdominal obesity, and irregular periods are usually seen along with ultrasound findings. By combining these symptoms and imaging results, the doctor can make a more accurate diagnosis. Many women may not have a clear ultrasound appearance but have clear clinical symptoms, or vice versa; For this reason, the interpretation of ultrasound should always be done along with the history.
Relationship between non-ovulation and ultrasound results
In women with ovarian laziness, eggs develop but are not released. This causes the follicles to remain around the ovary and their number can be seen more in the ultrasound. Lack of ovulation not only causes irregular periods but also can prevent pregnancy. Seeing numerous and small follicles without a dominant follicle is one of the clear signs of ovulation failure, which the doctor pays special attention to in the image.
Difference between cyst and follicle in ultrasound
One common mistake is to think of any round, dark spot on ultrasound as a "cyst," when in most cases what is seen is a follicle, not a true cyst. Follicles are normal and part of the ovulation cycle, but when their number increases, it is a sign of ovarian laziness. A true cyst is usually larger, with thicker walls and different contents. By examining the size and density of the image, the doctor can distinguish between the two.
Vaginal or abdominal ultrasound in the diagnosis of PCOS
In adult women, vaginal ultrasound is more accurate in examining the ovaries because the sensor is placed closer to the tissue. But in young girls or people who are not yet married, abdominal ultrasound is a safer choice. Sometimes the doctor suggests both types of ultrasound for a more detailed examination. In both methods, observing the time and experience of the doctor in interpreting the image is the most important.

Hormonal signs with ultrasound
Findings of ultrasound images become meaningful when they are examined together with blood tests. In women with PCOS, androgen and LH levels usually increase and FSH levels decrease. These changes cause the simultaneous growth of several follicles without ovulation. Therefore, ultrasound alone is not a definitive diagnosis, but must be combined with the examination of hormones and physical symptoms in order to obtain an accurate result.
Interpretation of the ultrasound report by the doctor
In the ultrasound report, terms like "multiple follicles", "ovary with increased volume" or "polycystic pattern" are usually seen. These expressions have a special meaning and weight for the doctor. The patient may be worried when reading the report, but only a specialist doctor can provide a correct interpretation according to the history and symptoms. Sometimes the presence of a few small follicles is normal and does not necessarily mean a disease.
Is ovarian laziness always seen in ultrasound?
No. In some women, the ultrasound may appear normal, but there are hormonal and clinical signs of ovarian indolence. This issue is seen especially in the early stages of the disease or in thinner women. In such cases, the doctor uses additional tests to evaluate the state of the ovary more accurately. The absence of symptoms in ultrasound does not always mean the absence of a problem; Scientific interpretation should be a combination of laboratory and visual data.
Differential diagnosis with similar diseases
Some conditions can create a PCOS-like image on ultrasound, such as simple ovarian cysts, benign tumors, or temporary changes caused by hormonal medications. Therefore, the doctor never makes a decision with just one ultrasound. Examining family history, weight, menstrual cycle and hormone levels helps to make a correct diagnosis. The distinction between these cases is very important, because their treatment methods are completely different.
The importance of ultrasound in the treatment follow-up
After starting the treatment, ultrasound plays an important role in evaluating the body's response. By comparing the images before and after the treatment, the doctor can determine whether the follicles are growing normally or not. In women receiving medication for pregnancy, this examination is even more important because it helps determine the exact time of ovulation. Continuing ultrasound follow-up makes the treatment path clearer and more accurate.
Relationship between age and severity of symptoms in ultrasound
Severity of symptoms of ovarian indolence usually does not decrease with age, but the ultrasound image may change. In young girls, follicles are usually more numerous and denser, while in women older than 30 years, the ovaries may be larger but with more scattered follicles. During menopause, the ovaries sometimes appear more normal, but their function is still impaired. Therefore, the interpretation of the findings should be done according to age and hormonal status.
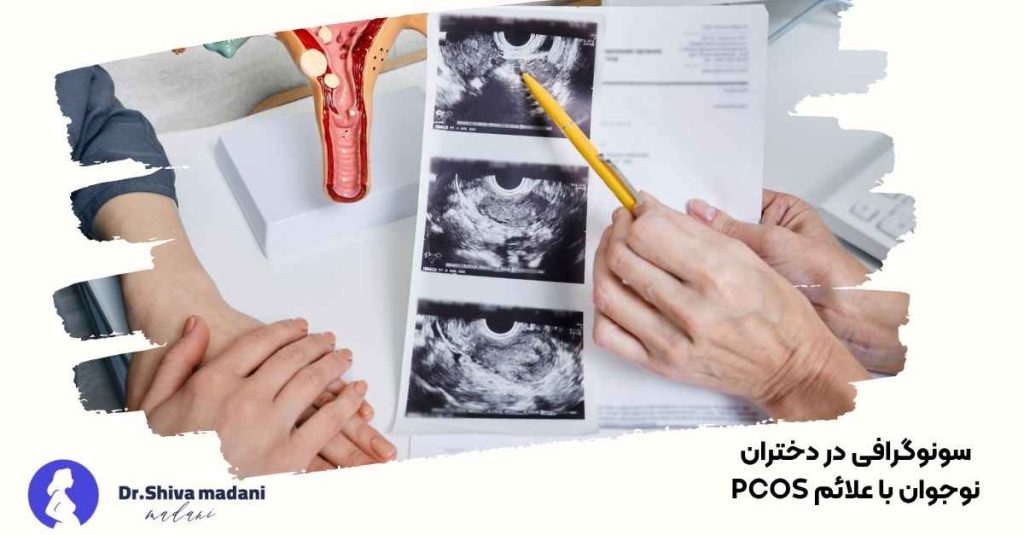
Ultrasound in adolescent girls with PCOS symptoms
In teenage girls, the diagnosis of ovarian laziness should be made more carefully because many hormonal changes are normal during puberty. At this age, the ovaries may be naturally larger and have multiple follicles. Therefore, the doctor will diagnose PCOS only if, in addition to the ultrasound findings, there are other symptoms such as irregular periods and increased hair loss. The approach in this age group is more based on follow-up and modification of lifestyle than drug treatment.
Warning signs of the need to see a doctor
If the menstrual cycle lasts more than 35 days, or there is no period at all, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and hormonal examination. Sudden weight gain, hair loss, or thick hair on the chin and face can also be warning signs. Many women live with these symptoms for years without knowing that the problem is the functioning of the ovaries. Going to the doctor early prevents more serious complications such as infertility or diabetes.
The role of lifestyle in the improvement of ultrasound findings
Changing lifestyle is one of the most effective ways to control symptoms of ovarian laziness. Losing even 5 to 10% of body weight can improve ovulation and reduce abnormal follicles in ultrasound. Regular physical activity, diet with low glycemic index and enough sleep play an important role in regulating hormones and improving ultrasound results. Sometimes, without the need for medicine, just by modifying the lifestyle, the ovary can be returned to normal function.
Effect of hormonal drugs on ultrasound
The use of hormone-regulating drugs, such as birth control pills, can change the appearance of the ovaries on ultrasound. These drugs temporarily reduce the number of follicles by reducing ovarian stimulation. For this reason, doctors usually recommend a baseline ultrasound to record the true state of the ovaries before starting the medication. Image interpretation during drug use should be done with caution as results may vary temporarily.
Relation of ovarian laziness with infertility
One of the most important consequences of PCOS is ovulation disorder and difficulty in pregnancy. In the ultrasound of these patients, tiny follicles are seen, but there is no dominant follicle that releases the egg. Fortunately, with appropriate drug treatment and careful ultrasound monitoring, the possibility of pregnancy is significant. By regularly checking the growth of follicles, the doctor can determine the best time for ovulation or assisted reproductive methods. Correct treatment has successful results in most cases.
The importance of early diagnosis with ultrasound
The sooner the diagnosis is made, the easier it will be to control the disease. Ultrasound is a tool that can show early changes in the ovary even before severe symptoms appear. Young women with a family history of PCOS should have an ultrasound once a year. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications such as infertility, weight gain, and type 2 diabetes.
The latest ovarian imaging methods
In recent years, in addition to two-dimensional ultrasound, Doppler and three-dimensional ultrasound are also used for a more detailed examination of the ovaries. Doppler helps the doctor see the blood flow to the ovary, and in certain cases, MRI can also be useful in differentiating between a cyst and a follicle. Nevertheless, ultrasound is still the most widely used and cost-effective method that will answer the diagnostic need in most cases.
Common mistakes of patients in ultrasound interpretation
One of the common mistakes is that patients think that the presence of several small follicles in the ultrasound means that they have ovarian laziness. While this situation may be temporary and caused by the natural changes of the menstrual cycle. Also, reading the ultrasound report without a doctor's opinion can cause unnecessary worry. Accurate interpretation is possible only when the doctor compares the symptoms and tests with the image.
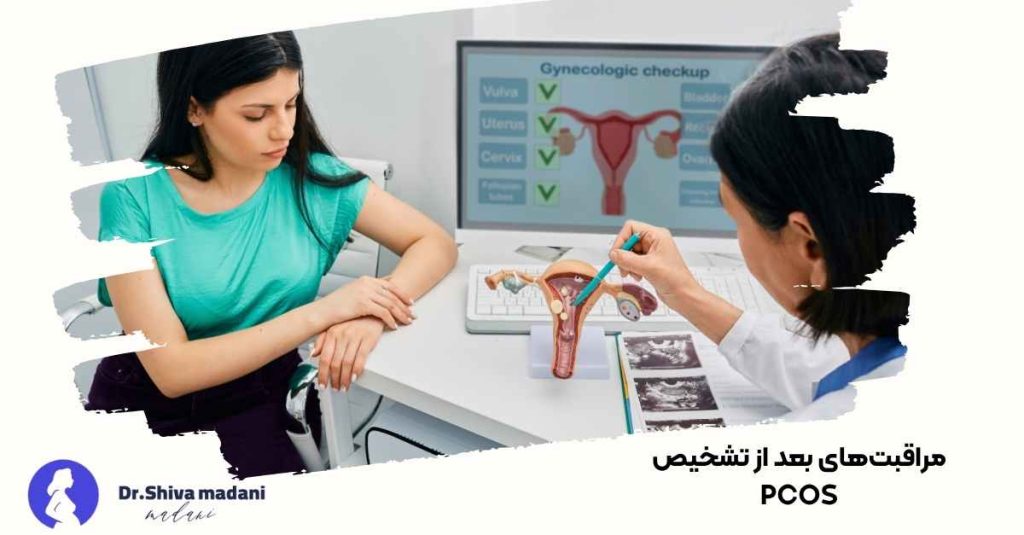
Care after PCOS diagnosis
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor offers a specific treatment plan based on the severity of symptoms and hormonal status. Taking hormone regulating drugs, weight control, and regular exercise are the main pillars of treatment. In addition, regular checkups and periodic ultrasounds help to check the progress of the treatment. Women should know that PCOS is not a lifelong disease; With proper care, symptoms can be controlled and the quality of life can be increased.
Summary
Ovarian laziness is one of the most common hormonal problems in women, and ultrasound is the most accurate tool for its diagnosis. In this method, the doctor can observe numerous follicles, increase in volume and thickening of the ovarian wall. Early diagnosis, following a healthy lifestyle and regular medical follow-up are the keys to successful management of this disease. If polycystic symptoms are seen in the ultrasound, don't worry; With appropriate treatment and gradual changes in lifestyle, the normal functioning of the ovaries can be returned. href="#">
Write your opinion Cancel Answer
Latest Articles

Care after vaginal RF
07/23/1404


blog Women's beauties Services Stay updated by subscribing to our newsletter
Stay updated by subscribing to our newsletter
مقالات دیگر از Dr. Shiva Madani Hosseini

Endometriosis from diagnosis to treatment
What is endometriosis? Replacement of the tissue of the inner wall of the uterus in other areas of the body is called endometriosis. There are four theories about the cause of endometriosis: ۱- اندوم...

Hymen or hymen
### Hymen or hymen Hymen is a membrane that covers the opening of the vagina. This word is a Greek word and is derived from the name of the goddess of marriage. In the initial embryonic stage, there...

Injection of gel into the vagina
One of the most common methods of vaginal rejuvenation is **injection of gel into the vagina**, due to women's satisfaction with the result of the operation, the demand for doing it is increasing. Pre...

Pain and swelling after labiaplasty
All people who do labiaplasty experience pain and swelling in the operation area, and this is completely normal. The swelling and inflammation that occurs after labiaplasty and its severity can be lo...

Suitable people for labiaplasty
What is labiaplasty? Labiaplasty is performed to reduce the size of the labia and to improve the beauty and condition of the labia, but the question that arises is who are suitable for labiaplasty, th...

What are stretch marks or stretch marks?
stretch marks or stretch marks Stretch marks or striae are skin lesions that appear in the form of lines in the thighs, hips, abdomen and breasts due to thinning of the skin and indentation of the s...

Anatomy of the female reproductive system
Knowing the anatomy of the female reproductive system will help women to have a better understanding of the condition of their organs so that if they see a problem in that organ, they can take better...

What is premenstrual syndrome or PMS?
What is premenstrual syndrome or PMS? It is a group of physical and mental symptoms that occur periodically and close to menstruation in women. About 75% of women suffer from mild premenstrual syndrom...

Vaginal infection
Vaginal infection is one of the most common reasons for visiting a gynecologist, which is caused by the disruption of the microbial balance of the vagina. In this article, after introducing the types...

Urinary tract infection in women
Urinary tract infection is an infection that involves the urinary tract including: urethra, bladder and kidneys. They are parasitic, bacterial, fungal or viral infections. Urinary tract infections th...

Reason for delayed period
What is the reason for delayed period? In general, the main and common reasons for delayed periods are: - **Stress** - **weight fluctuations** - **Hormonal disorders** - **pregnancy** - **use of dru...

Gestational diabetes from diagnosis to treatment
Complications of gestational diabetes - Birth of a baby with high weight (macrosomia) - Abortion - stillbirth - Pregnancy toxicity (pre-eclampsia) Cause of gestational diabetes During pregnancy, ho...

SEO site management services
Search engine optimization (SEO) services help you to rank your website higher in the search results of Google and other search engines.

Implementation of branding and digital advertising
Digital branding means creating a strong and distinctive brand in the digital space for a company or a specific product. This process involves using digital methods and strategies to build and strengthen the brand.

Website design for companies and businesses
Website design for companies and businesses can help you have a stronger online presence and attract more customers. Contact us for more information.
